Features
The History and Meaning of Valentine’s Day

Valentine’s Day, celebrated annually on February 14, is a day dedicated to love and romance. This year, it falls on a Friday. Across the United States and many parts of the world, people exchange candy, flowers, and gifts as symbols of affection, all in the name of St. Valentine.
But who was St. Valentine, and where did these traditions originate? The history of Valentine’s Day is a fascinating blend of legend, ancient rituals, and historical events.
The story of St. Valentine remains shrouded in mystery. The Catholic Church recognizes at least three different saints named Valentine or Valentinus, all of whom were martyred. One of the most widely accepted legends tells of a third-century Roman priest named Valentine. When Emperor Claudius II ruled that single men made better soldiers and banned marriage for young men, Valentine defied the decree by secretly performing weddings. When his actions were discovered, he was imprisoned and later executed.
Another version suggests that Valentine was a bishop named Valentine of Terni, who was also executed by Claudius II. Yet another tale claims Valentine was martyred for aiding persecuted Christians. Before his death, he allegedly sent a letter signed “From your Valentine” to a young woman possibly his jailer’s daughter thus inspiring the modern phrase.
While the truth behind these legends is uncertain, St. Valentine became a symbol of love, courage, and devotion. By the Middle Ages, he was one of the most popular saints in England and France.
Valentine’s Day may have deeper roots in the ancient Roman festival of Lupercalia, celebrated from February 13 to 15. This fertility festival involved rituals meant to ensure health, ward off evil spirits, and encourage prosperity. Men sacrificed goats and dogs, then used the hides to whip women, believing it would promote fertility. The festival also included a matchmaking lottery, where young men and women were paired off.
As Christianity spread, Pope Gelasius I sought to replace the pagan festival with a Christian observance, officially declaring February 14 as St. Valentine’s Day in the late 5th century. However, the romantic associations of the day did not fully take shape until much later.
By the Middle Ages, people in France and England believed that February 14 marked the beginning of birds’ mating season, further reinforcing the idea that the date should be associated with love and courtship. The English poet Geoffrey Chaucer was among the first to link St. Valentine’s Day to romance in his 1375 poem “Parliament of Fowls,” writing:
“For this was sent on Seynt Valentyne’s day / When every bird comes there to choose his mate.”
By the 15th century, written love notes became popular. The oldest known valentine, a poem penned by Charles, Duke of Orleans, to his wife in 1415 while he was imprisoned in the Tower of London, still exists today in the British Library. Later, King Henry V is believed to have hired a writer to compose a romantic note for Catherine of Valois.
The tradition of exchanging valentines gained widespread popularity during the Victorian era. By the mid-19th century, mass-produced Valentine’s Day cards became common, thanks to innovations in printing and postage.
Cupid, the mischievous cherub often seen on Valentine’s Day cards, has origins in Roman mythology. He is based on Eros, the Greek god of love, who was originally depicted as a handsome, immortal being capable of making gods and mortals fall in love with his golden arrows. Over time, particularly during the Hellenistic period, Eros transformed into the chubby, childlike figure we recognize today.
By the 18th century, Valentine’s Day had become firmly established as a celebration of love in England, and it soon spread to the United States. During the 1830s, businesses began selling pre-made Valentine’s Day kits. By the late 19th century, commercialism had taken hold.
The holiday’s commercial boom escalated in the 20th century, with greeting card companies, florists, chocolatiers, and jewelers heavily marketing the occasion. Today, Valentine’s Day is a multi-billion-dollar industry, with people purchasing cards, flowers, chocolates, jewelry, and even extravagant experiences to celebrate love.
In modern times, Valentine’s Day has expanded beyond romantic love to include expressions of affection for family, friends, and even self-love. The holiday has become a cultural phenomenon, embraced worldwide in various forms. While some cherish its traditions, others criticize its commercialization.
Regardless of its origins whether rooted in Roman festivals, Christian martyrdom, or poetic traditions Valentine’s Day continues to be a day devoted to love, passion, and human connection.
Business
The Meta Trap: How One Bot Strike Can Liquidate Your Digital Career
As a digital communicator, this ban doesn’t just erase a social profile; it obliterates gigs and revenue streams.
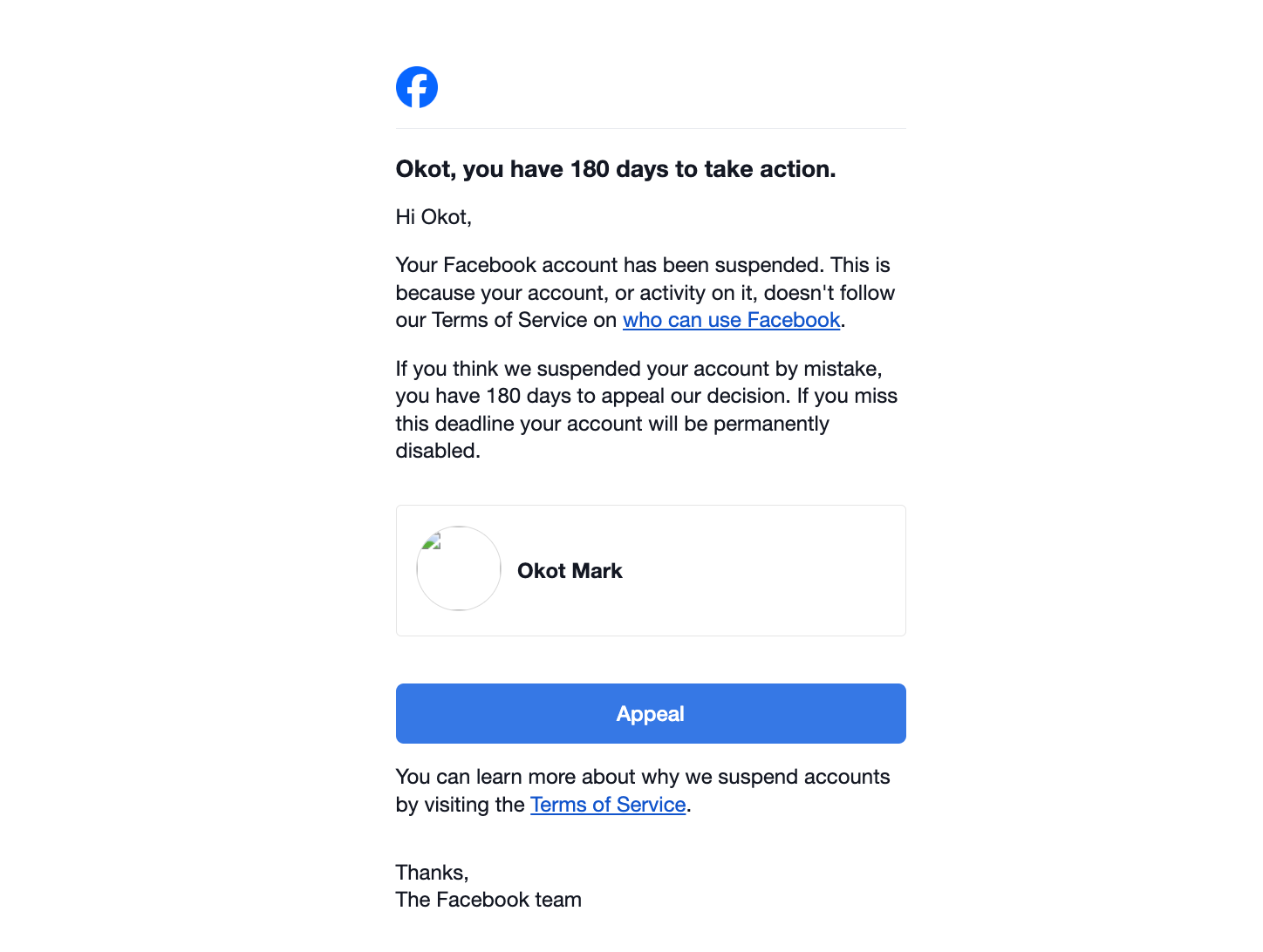
In the fast-paced world of digital communications and marketing, your online presence is your livelihood. For me, it was the foundation of multiple businesses: a music artist page, a clothing brand, a design company, and numerous client accounts. But on December 9th, everything changed with a single email from Meta. What started as a routine suspension notice escalated into a permanent ban overnight, stripping me of access to my entire professional ecosystem. No explanation. No recourse. Just gone. This isn’t just my story, it’s a cautionary tale for anyone relying on Meta’s platforms for their career.
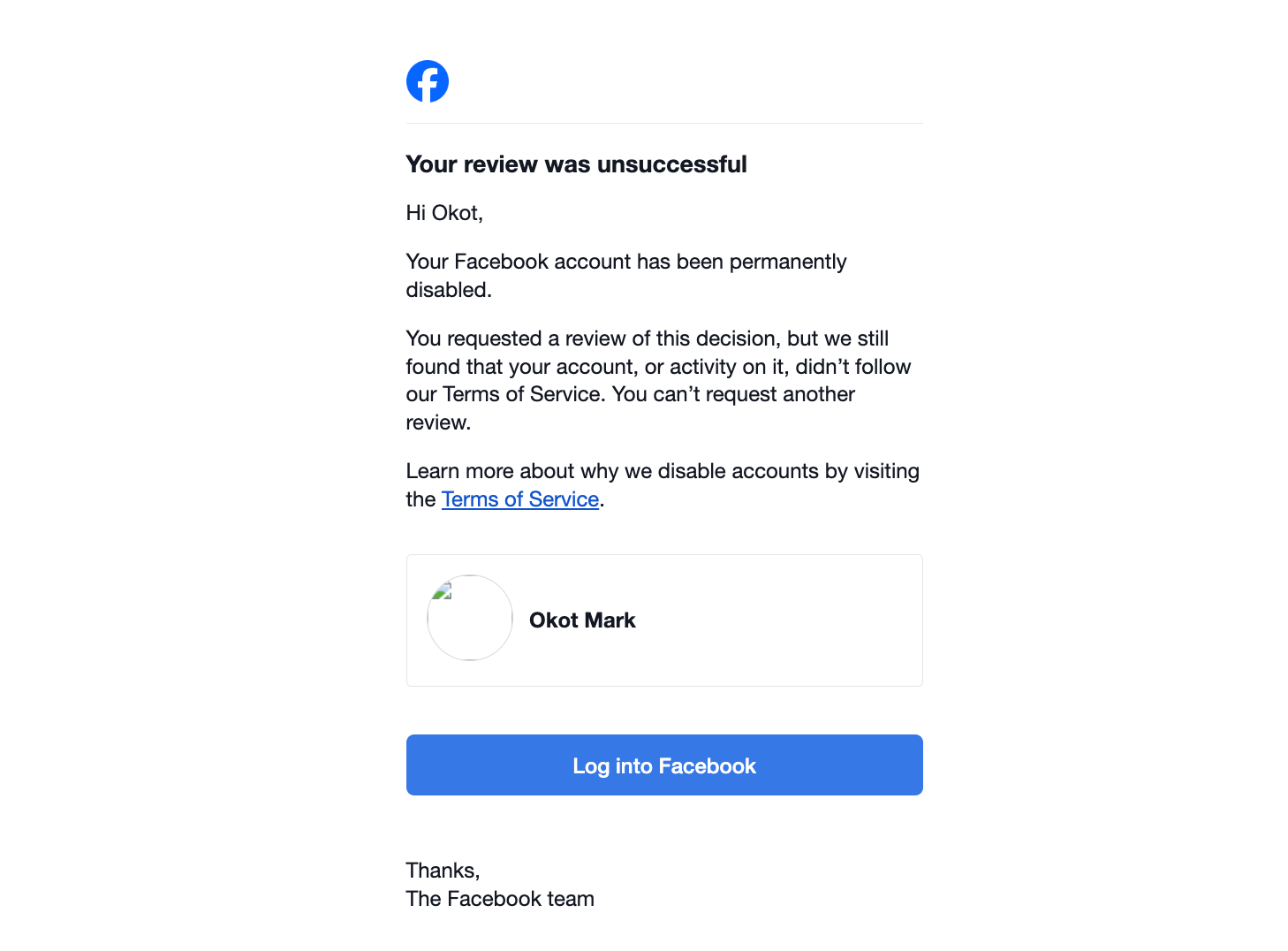
I arrived home that evening to find an email from Meta notifying me that my Facebook account had been suspended. It urged me to appeal within 180 days, or face permanent deletion. Puzzled but proactive, I submitted my appeal immediately. By the next morning, another email arrived: my account was permanently disabled, and the appeal had been denied. No reasons were provided, just a cold statement that I’d lost access forever.
I rarely posted personal content on Facebook. My account was primarily a gateway to Meta Business Suite, the hub for managing professional pages across Facebook and Instagram. Through it, I controlled a suite of business assets: my own ventures and those of my clients. As the sole full admin, I handled everything from content scheduling to campaigns. Little did I know, this setup was a ticking time bomb.
When you create a page on Facebook or Instagram, linking them via Meta Business Suite creates a unified Business Portfolio. This is the command center for your digital empire. It allows you to manage pages, grant roles to team members, and integrate tools like WhatsApp Business Platform for large-scale operations. Third-party services often require access to this portfolio to function properly.
The problem? Meta’s system ties these portfolios tightly to personal accounts. When my account was banned, I was automatically removed as the full admin, leaving the role vacant. Suddenly, Meta held sole control over my pages and client portfolios. Attempts to log in via Instagram offered limited access, but I couldn’t remove the banned account or promote another user to full control.
Desperate for resolution, I reached out to Meta’s support; only to discover it’s virtually nonexistent for issues like this. Human responses (when they came) were unhelpful. Many online forums suggested subscribing to Meta Verified on Instagram as a workaround, but that didn’t resolve the core issue. I even filed countless “Admin Dispute Claims,” providing every requested document: business registrations, IDs, proof of ownership. Their response? They couldn’t manually promote another admin because the original account was banned. The exact reason I was disputing in the first place!
This circular logic is infuriating. Online communities are rife with similar complaints: Meta’s automated bots flag and delete accounts without transparency or appeal processes that actually work. Some advise assembling a legal team to confront Meta directly, arguing that they’re effectively holding your digital assets hostage. In my case, that’s exactly what happened. I lost control of my music page, clothing brand, design firm, and client accounts overnight, all without a single violation explained.
As a digital communicator, this ban doesn’t just erase a social profile; it obliterates gigs and revenue streams. Clients rely on seamless access to their ad data, analytics, and campaigns. Without it, projects stalled, trust eroded, and opportunities vanished. Researching further, I found this is a widespread epidemic. Countless marketers, creators, and small business owners have shared horror stories on forums like Reddit and X (formerly Twitter). Meta’s opaque algorithms and lack of accountability have led to lost livelihoods, with users begging for reasons that never come.
The stakes are high in an industry where platforms like Meta control the gates to billions of users. One unjust ban, and your life’s work evaporates. It’s not just about losing followers; it’s about Meta seizing ownership of your Business Portfolio and refusing to relinquish it.
If you’re in digital marketing or communications, don’t wait for the dreaded email. Here’s how to safeguard your assets:
- Distribute Admin Roles Wisely: Grant full admin rights in your Business Portfolio to a few trusted colleagues or partners. This creates redundancy, so a single ban doesn’t lock everyone out.
- Create Backups: Set up duplicate pages or alternative accounts as contingencies. Mirror key content and audiences where possible.
- Disassociate Personal and Business Accounts: Where feasible, unlink your personal Facebook account from business pages. Use dedicated business profiles to minimize risk.
- Diversify Platforms: Don’t put all your eggs in Meta’s basket. Build presence on alternatives like LinkedIn, TikTok, or X to mitigate total loss.
- Prepare for the Worst: Document everything, screenshots of access, business proofs and consider legal consultation early. It is said that Meta responds better to formal demands than support tickets.
Meta’s ecosystem is powerful, but it’s also precarious. One day, without warning, they could claim full ownership of your digital portfolio and refuse to give it back. My experience proves it. Don’t let it happen to you, act now to secure your future in this volatile online world.
Features
Why Artists Turn to Drugs

The dream starts brightly: a song, a stage, a legacy. For countless artists, it’s a fire that burns hot until it doesn’t. Take Josh not his real name, but a true soul who’s been there. Fresh from university with a Bachelor’s degree in Industrial and Fine Art, he didn’t settle for a cubicle. “I wanted to create everything,” he says, his voice steady but heavy with memory. “The music, the videos, the designs, I’d be the whole machine.” As a songwriter and producer, he plunged into the industry, hunting for the hit that would make his name. But the climb was slow, and the years bled into each other as he sold beats for pennies and stacked unreleased songs that gathered dust.
By the age of 30, Josh had little to show but a few indie tracks and a growing ache from time lost. Then COVID hit, silencing the world and his hustle. Gigs vanished, pitched songs stayed shelved, and depression crept in like a shadow. “I was fighting wars that weren’t mine,” he says, “caught in industry politics, losing allies over things I couldn’t fix.” Drugs slipped in quietly not as inspiration, but as a way to mute the regrets piling up. “I should’ve taken that job after school,” he admits. “It would’ve kept me fed while I figured this out.”
Josh’s story isn’t unique, it’s a refrain echoed across the creative world, from bedroom studios to sold-out arenas. In Uganda, whispers circulate about Geosteady, the Afrobeat star behind “Owooma” and “Tokendeeza.” claiming he’s in rehab hint at a battle with addiction. It’s unconfirmed, just speculation, but it fits the pattern of an artist under pressure, teetering on the edge. Whether true or not, it raises a lingering question: Why do so many artists turn to drugs?
The answers aren’t simple, but they’re rooted in the crucible of the creative life. The pressure to produce is relentless, each track becomes a gamble on relevance, and every year without a win is a weight on the soul. For Josh, it was the grind of waiting for a break that never came. Research supports this; the Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment links high-stress creative fields to substance use as a coping tool. The National Institute on Drug Abuse adds that mental health struggles like the depression and anxiety Josh faced double the odds of reaching for a fix.
The culture plays a part as well. Music scenes can feel like a nonstop party, where drugs are as common as the beat drops. “It’s just there,” Josh says. “You don’t always choose it, it chooses you.” And then there’s the myth of the “tortured artist,” suffering for art’s sake. Society consumes this notion, think Hendrix, Winehouse turning pain into legend. But Josh shakes his head. “It’s not art, it’s survival. You’re not creating better; you’re just hurting less.”
For Josh, the spiral may have looked like depression feeding substance use, a diagnosis too common among artists. The instability of the gig economy, the emotional toll of rejection, and the quiet despair of “what if” nudged him toward escape. Alcohol could have been the start; harder substances, a deeper dive. Recovery meant stepping back. “I got a job and it was nothing fancy, just steady,” he says. “I wrote on my terms. Therapy helped when I could get it.” Not every artist has that lifeline; access to support varies, and in places like Uganda, resources can be scarce.
This story isn’t new, but it’s human. It’s Josh, staring down a decade of “what ifs.” It’s the whispered rumors of a star like Geosteady, whether true or not. It’s the push and pull of creation and collapse, played out in studios and souls worldwide. “I wish I’d known it didn’t have to be all or nothing,” Josh reflects, holding a quiet hope for those still in the fray. For every artist teetering on the edge, the prayer is that the music doesn’t fade to silence but rises again, stronger.
Blog
How Mobile Money is Reshaping an Entire Economy
The growth of the fintech sector hasn’t been limited to the dominant players in mobile money. New entrants have emerged, offering asset financing for small businesses and digital platforms for community savings, thereby diversifying the landscape.
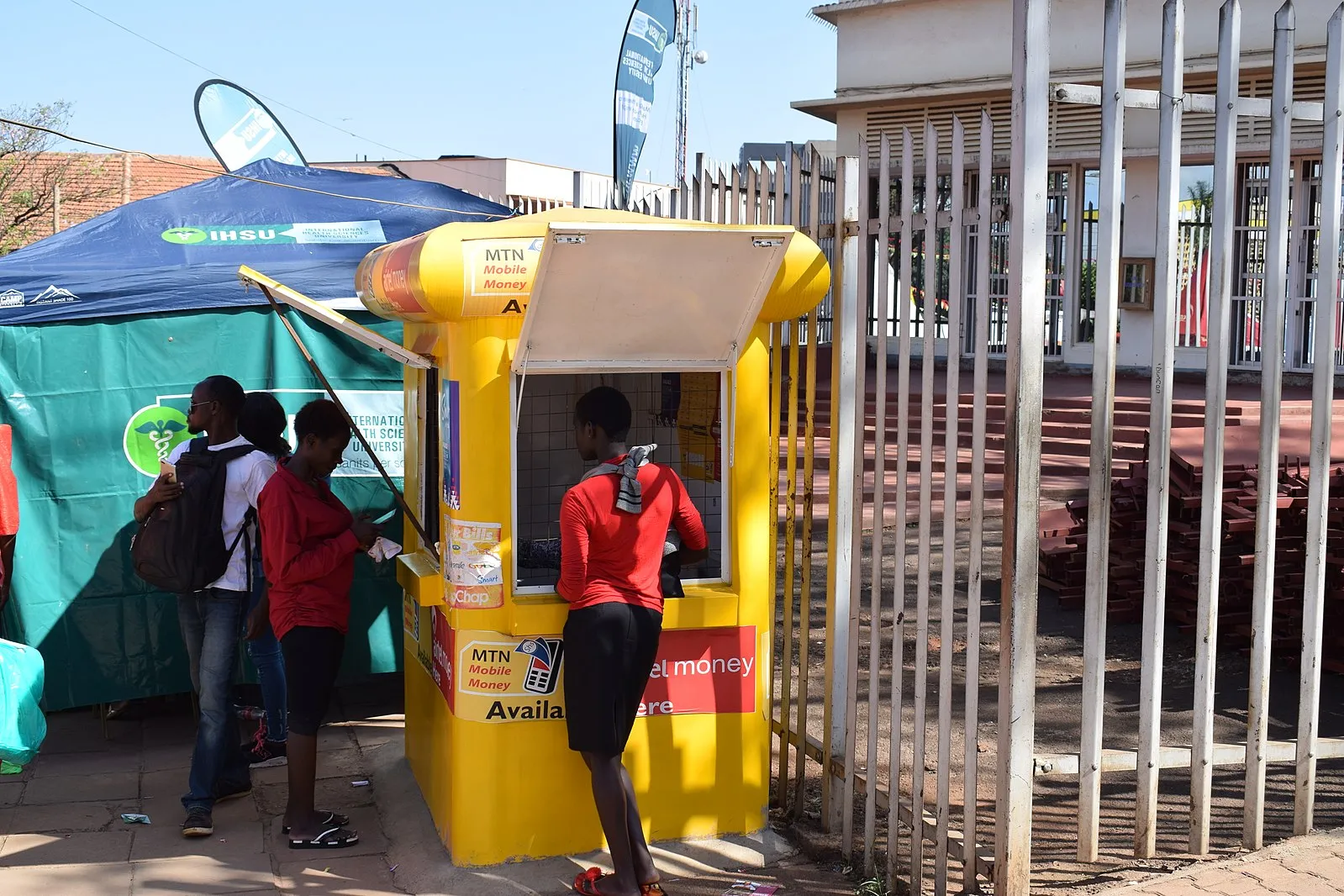

In the bustling streets of Kampala and the serene villages of rural Uganda, a financial revolution has been quietly unfolding, driven by the rapid rise of fintech, with mobile money at its core. By March 6, 2025, this transformation has established Uganda as a leader in digital innovation in East Africa, reshaping how millions save, spend, and envision their futures.
The movement began with the unbanked, those living far from the brick-and-mortar banks typically found in urban areas. In a country where nearly 70% of the population previously lacked access to formal financial services, mobile money emerged as a vital solution. Platforms like MTN Mobile Money and Airtel Money transformed basic cell phones into digital wallets, enabling farmers in Gulu to pay for seeds, traders in Mbale to settle bills, and families in Lira to receive remittances from relatives abroad. By 2025, the transaction values had soared past 90% of Uganda’s GDP, highlighting how profoundly this technology has integrated into daily life.
The advancements in mobile money are remarkable. What started as simple peer-to-peer transfers has evolved into a sophisticated ecosystem. Collaborations between telecom giants and banks have led to the creation of products like micro-loans and savings accounts, all accessible with just a few taps on a phone. A boda boda driver in Kampala can now borrow funds instantly to repair his motorcycle, with repayment tied to his daily earnings, while a savings group in Masaka can digitally manage its contributions, reducing the risks associated with handling cash. These innovations have driven a surge in financial inclusion, bridging gaps that traditional banking could not reach, particularly in rural areas where mobile penetration surpasses physical banking infrastructure.
The growth of the fintech sector hasn’t been limited to the dominant players in mobile money. New entrants have emerged, offering asset financing for small businesses and digital platforms for community savings, thereby diversifying the landscape. The government and regulatory bodies have also played a crucial role, fostering an environment where these services can thrive. Policies that promote digital transactions and the formation of financial technology associations have facilitated this growth, ensuring that, even as costs rise, prompting firms to pass charges onto clients. The sector remains resilient. Reports circulating on March 6, 2025, noted improved business conditions in Uganda’s private sector, with fintech’s dynamism acting as a quiet driver behind the scenes.
However, this rise has not been without challenges. A hacking incident earlier in 2025 resulted in millions being siphoned from the central bank’s systems, exposing vulnerabilities in the broader financial framework. Yet, the decentralized nature of mobile money kept it active, with its users largely unaffected by the breach. Meanwhile, the central bank’s steady management, maintaining firm lending rates amid global uncertainties, has kept inflation in check, hovering between 4% and 5%, providing a stable backdrop for fintech’s expansion.
The promise of this fintech boom extends beyond financial statements. With ambitions to grow the economy to nearly $60 billion by mid-2025, leaders view digital finance as a cornerstone of that vision. Every transaction from a shopkeeper in Kampala selling airtime to a farmer purchasing fertilizer brings the nation closer to that goal. Nonetheless, challenges remain: high fees, inconsistent rural connectivity, and gaps in digital literacy could hinder momentum. Still, the prevailing sentiment is clear. Mobile money and its fintech extensions are thriving, driving a financial evolution that is as much about empowerment as it is about economic growth.
As Uganda stands on this digital frontier, the rise of fintech, fueled by advancements in mobile money, signifies more than just a trend. It is a movement that redefines wealth and opportunity, one phone at a time.
-

 Entertainment12 months ago
Entertainment12 months agoMuseveni’s 2025 Copyright for Musicians breakdown
-

 Business12 months ago
Business12 months agoUganda’s Ministry of Finance projects significant growth opportunities in 2025
-

 Policies12 months ago
Policies12 months agoBreakdown of the Uganda Police Force Annual Crime Report 2024
-

 Sports11 months ago
Sports11 months agoThe Transformative Impact of World Cup Qualification for Uganda
-

 Policies12 months ago
Policies12 months agoIs Uganda’s Shs10m Fine the WORST Thing for Cohabiting Couples?
-
 Health12 months ago
Health12 months agoBreaking down the Malaria Vaccine Rollout in Uganda
-

 Business12 months ago
Business12 months agoThe 9 worst mistakes you can ever make at work
-

 Entertainment12 months ago
Entertainment12 months agoIsaiah Misanvu Teams Up with Nil Empire for a Soul-Stirring Anthem of Gratitude and Transformation “Far Away”